Study Quantifies Modular's Wood Waste Savings
A recent study commissioned by MBI and carried out at Colorado State University shows that when it comes to optimizing the circular economics of a construction project, modular is the preferred way to build (when compared to traditional ground-up framing techniques). Now, this isn’t new information for those in the modular community. The very nature of using modular construction techniques is that there is less material waste. But this new study will help quantify that savings.
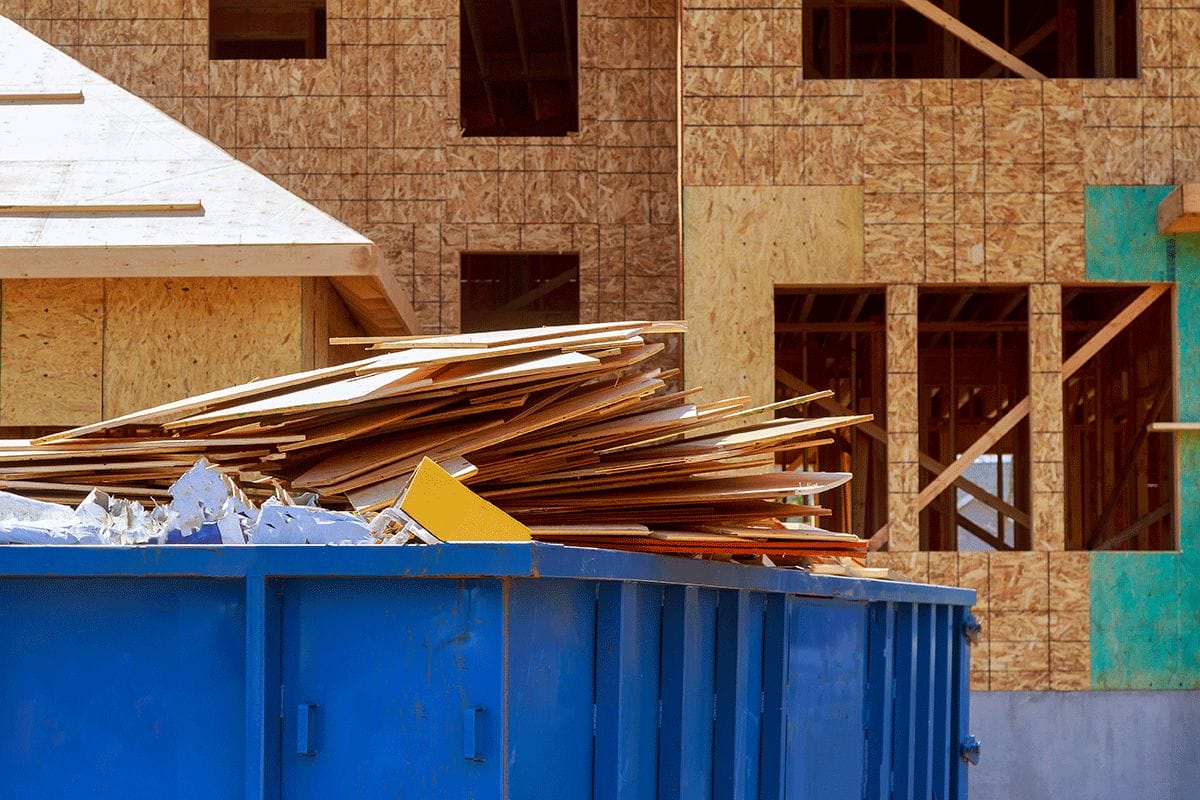

Killingsworth’s research compared the raw weight of lumber removed from the job site (roll-off weight of dumpsters processed by the waste hauler) with the wood waste created at the modular plant. Those amounts were then divided by the square footage and the total wall height of each project to come up with an average amount of waste.
The study compared the wood waste (in weight) created by two multifamily projects, one using modular construction and the other
traditional stick building. It then calculated the amount of wood waste created by framing activities when compared to both the square
footage and the wall height of each project. This was done in order to provide a consistent comparison, as the ceiling heights on the stick-built project varied.
The research team made several visits to the stick-built site to ensure that wood waste was being properly sorted. At times they found
additional materials and refuse in the wood waste dumpster, so they continued to monitor sorting throughout the project. They also visited the modular manufacturing plant, which had just instituted a waste sorting and reduction process, and confirmed that the process was being followed. Because the process was being followed so closely at the plant, they didn’t revisit it as often.
The results, which will be released at MBI’s 2024 World of Modular, show that modular construction does a better job of keeping wood waste out of the landfills. The research compared the raw weight of lumber removed from the job site (roll-off weight of dumpsters processed by the waste hauler) with the wood waste created at the modular plant. Those amounts were then divided by the square footage and the total wall height of each project to come up with an average amount of waste.
When asked if he was surprised by this result, John Killingsworth, associate professor in the construction management program at CSU, said no. “To be a good scientist you want to be unbiased and have an open mind to accept whatever the data says, and we were. We took two measurements, square footage and ceiling height, to ensure that the data is compared equally. But, no, I wasn’t really surprised.”
The results stand even though modular construction uses more overall lumber than stick framing.
By its nature, modular multifamily developments have twice the ceilings, floors, and walls as stick framing. This is one of the major advantages of using modular, as it reduces noise transmission, leading to quieter living spaces.
The wood waste study was primarily backed by MBI with some assistance from the university. Killingsworth hopes modular construction companies and designers will use this data to market the advantages of modular construction and help grow its market share.
Killingsworth comes to his teaching role with a background in the trades. He worked in the field for 16 years and gained skills in both project management and site management, before going back to school to get his advanced degree. After earning his PhD at the University of Nebraska, he taught in Wisconsin for a few years before moving to Colorado State University.
He is no stranger to modular construction or construction research. During his time in Nebraska, he worked under a Department of Labor grant to provide workforce development focused on modular construction. Then, after he moved to Colorado, he participated in a Department of Energy grant-funded study that compared the energy performance of traditional stick-built multifamily construction with modular, specifically in areas where energy codes are strict (California, Pennsylvania, and Seattle, Washington). The final results of this study, which will be released soon, show that modular performed better. And the relationships with modular builders that were created in that study were leveraged in the recent MBI study on wood waste.
Killingsworth uses his early experiences in the field to give his students context to what they’re learning. The construction program at CSU focuses on the dynamics of construction management at many levels, including superintendent, project manager, and during preconstruction. Topics include estimating, scheduling, contracts, quantity take offs, BIM tools, and construction finance. Students are required to complete two summer internships, which gives them more exposure to the real world and helps with job prospects. The majority of CSU graduates will go into commercial construction management, whether for general contractors or trade contractors.
As far as future research is concerned, Killingsworth hopes that the industry will look at the potential waste savings for other building materials, like steel, or product packaging, like cardboard and Styrofoam. He’d also like to see the industry study the labor savings of modular versus traditional construction. “We don’t really have any empirical data to speak to that. And if we’re going to have a true conversation on circular economics, it’s not just materials, but we’ve got to look at labor efficiencies and the financial impact.”
“We can argue about the improved quality of modular construction, the better energy performance, the lower environmental impact, and the reduced waste, and those are easy arguments to win. But ultimately, if the owner can’t make as much money, then it’s difficult to change their mind. So that’s why I would love to be able to specifically say modular construction is actually equal to or less expensive than traditional construction when you consider the time value of money and lifecycle costs.”
Killingworth intends to use his upcoming sabbatical next year to dive into more specific research on circular economics and construction. A circular economy looks to keep products and materials in service for as long as possible. It focuses on reducing material use, redesigning materials and products to be less resource intensive, and recapturing waste as a resource to manufacture new materials and products. In 2009, the EPA and other federal government agencies adopted a sustainable materials management approach that embraces circularity. The ultimate goal is to transform how we view and handle natural resources, materials and products, and waste. Their vision is a waste management system that is inclusive, more equitable, and reflects the urgency of the climate crisis. Modular construction can be at the forefront of this vision.
Only at World of Modular:

Waste Reduction Practices in Multifamily Construction
John Killingsworth, Associate Professor, Department of Construction Management, Colorado State University
Modular, offsite, and prefabrication practices are growing at a faster pace than traditional construction methods because these innovative solutions address concerns around workforce limitations, material supply-chain, safety, and quality. Past research efforts have typically focused on the qualitative rather than quantitative aspects of modular construction. This research gap provides an opportunity to leverage existing relationships with developer and modular communities to truly measure the quantitative benefits of offsite construction.
Colorado State University has completed a comparative study seeking to specifically measure framing material waste produced during a traditional site-built multifamily project and a modular offsite-built multifamily project. This comprehensive research outlines the significant limitations that exist in traditional building and waste management systems, and the increasing advantages that modular construction practices have in these processes. The research will provide actionable data for modular construction experts and novices alike.
About the Author: Dawn Killough is a freelance construction writer with over 25 years of experience working with construction companies, subcontractors and general contractors. Her published work can be found at dkilloughwriter.com.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.