The Envelope Insulation Design Regarding Material Alteration Compatibility in Blast-Resistant Modular Buildings

Ran Yu is an arcitect with GLMV Architecture
Blast-resistant modular buildings (BRM buildings) are designed with strong steel exterior wall structure and thick steel skins to withstand blast events and to protect people and equipment from explosions. They are commonly used in oil refineries, chemical processing plants, laboratories, and similar operations.
However, the intrinsic high thermal conductivity of the steel skin and structure in exterior walls acts as the cold bridge reducing the efficiency of building envelope insulation. This results in the need for more insulation material and thicker insulation layers for BRM buildings to comply with building energy code. As energy code and energy-saving standards are adopted by more and more jurisdictions, the requirements for energy code compliant building envelope insulation design have increased.
Meanwhile, the module dimension of modular buildings adopts the inherent limitation of transportation. The prevailing transport limit is 12 feet wide and 40 feet long. A modular unit exceeding this limitation will result in a significant increase in shipping costs.
The third challenge of BRM insulation design is the suddenly derailed global supply chain with price and availability uncertainty. Following the pandemic, the existing global supply chain developed over the past decades was challenged and forced to reshuffle within a few years. The construction industry is experiencing insulation material shortages and incredible price increases. This leads to three possible results: spending extra time and money to redesign and revise drawings with alternative insulation materials; increased construction budgets; postponement or cancellation of projects.
Thus, BRM envelope insulation configuration has impacts on construction schedule time, potential redesign workload, and market competitiveness, which are all critical to the success of a BRM project. One must ask then, how to design an envelope insulation fitting in BRM exterior wall, being compatible with material alteration without wall thickness increasing?
The Envelope Insulation Design Regarding Material Alteration Compatibility
Design for material alteration compatibility aims to reduce redesign, project postponement and cancellation by thinking ahead. At the outset of a project design, consider various insulation material options and thicknesses available
and their impact to energy code compliance. This allows better coordination with blast-resistant structural design requirements. Different than using determined insulation material, design for material alternation compatibility requires the study of various insulation material properties, unit price, and their compatibility with current factory equipment and worker’s skill. The design process is below:
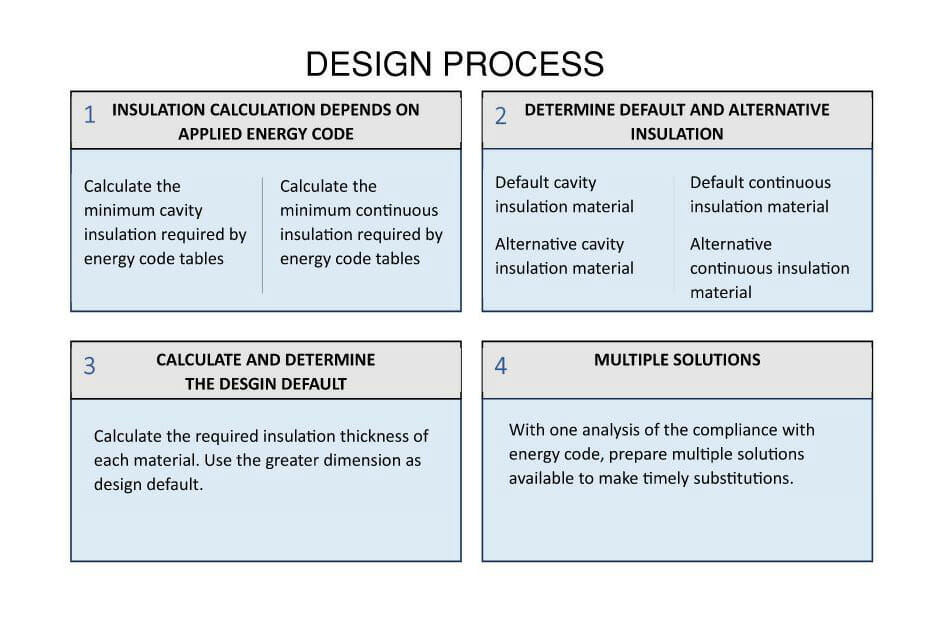
- Insulation calculation depends on applied energy code.
(1) Calculate the minimum inorganic cavity insulation between steel framing required by energy code tables.
(2) Calculate the minimum continuous insulation required by energy code tables. - Determine default and alternative insulation materials.
In BRM buildings, to achieve energy code compliance, cavity insulation is needed in between steel framing, and continuous insulation is needed to be attached to the inner side of steel structure. All these are done without changing BRM’s inherent structural characteristics. At least two materials each for the cavity and the continuous insulation shall be selected.As an example of material selection, one may use close-cell spray foam or mineral wool as cavity insulation, while using polyisocyanurate rigid board or extruded polystyrene board as continuous insulation.
- Calculate the required insulation thickness of each alternative material. Use the greater dimension as design default.
- Now with only one analysis of the compliance with energy code, we have multiple solutions available to make timely substitutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, design BRM building envelop insulation with compatible to alterative materials supports the success of BRM projects by reducing postponement and cancellations due to redesign work and time, controlling project budget and time.
These advantages will benefit all stockholders including building owners, contractors, manufacturers, and designers.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.