How Climate Change Will Impact Existing Fleet Units – Brace Yourself!

Tom Hardiman, CAE, is the Executive Director of the Modular Building Institute.
Several years ago, MBI worked with the ICC to get language included in the International Building Code to protect existing fleet assets from having to be brought up to new codes upon relocation. Many code officials applied the “moved structures” section of the IBC to fleet units being relocated.
MBI worked to eliminate the “moved structures” section completely form the IBC and added a new section (3113) specific to relocatable buildings. That section of the code, included in the 2018 IBC, makes it clear that any newly constructed relocatable building must comply with the code for new construction. However, any existing building, one for which a permit has been pulled, is governed by Chapter 14 of the International EXISTING Building Code (IEBC) not the IBC.
General contractors, new to modular construction, were on the hunt for presentations that might help answer questions about how to efficiently and effectively get started in the offsite industry. The Lounge proved to be a fruitful space to connect GC’s with other organizations to teach, learn, and collaborate. If we want to grow our industry we need to consistently create easily accessible training resources and make sure we are making space for this type of learning at offsite conferences.
Pittsburgh-based Module has been working on training standards since their launch of the Last Mile Network that includes the manufacturers, architects, transporters, and GC’s who are trained on the MODULE building system. The resulting training manual, the Off-Site Construction Playbook, includes sections on Design & Pre-Construction, Site and Set Day Prep, On-Site MEP Connections and Completion, and Post-Set On-Site Finish Work. Module is now helping other companies create their own Playbooks.
In summary, Chapter 14 states that any building relocated into an area must comply with the applicable site conditions, namely wind, snow, seismic, and flood hazards. By including this “grandfathering” provision for existing fleet, MBI has been able to protect these assets and allow them to continue to be used, so long as they meet the local site conditions.
This rarely has posed any issues for our industry, because how often do wind, snow, and seismic requirements change after all? Well….as it turns out, some jurisdictions are looking at their site requirements due to the impact of climate change on buildings. Here’s a few ways climate change is impacting existing building inventory:
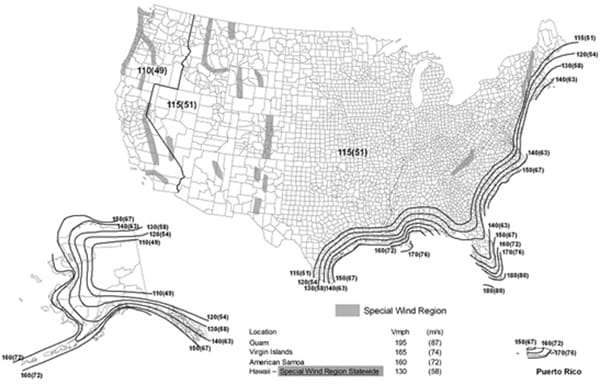
2015 IBC 1609.3 Ultimate design wind speed.
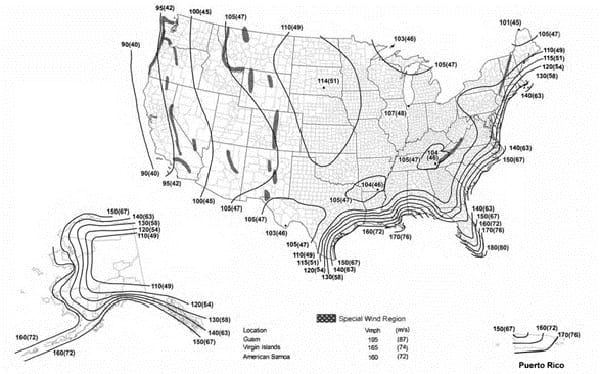
2018 IBC 1609.3 Basic design wind speed.
- Higher temperatures can lead to increased cooling demands, which can strain HVAC systems and lead to higher energy, maintenance, and / or replacement costs.
- Stronger storms, hurricanes, and floods can damage building exteriors, foundations, and infrastructures like drainage systems. This can lead to more frequent repairs and higher maintenance costs.
- Increased precipitation and humidity can lead to issues like mold growth, rot, and deterioration of building materials as well as impacting indoor air quality and occupant health.
- In regions where temperatures fluctuate around the freezing point, more intense freeze-thaw cycles can cause cracks in foundations, walls, and pavements, leading to structural damage.
- As climate patterns shift, buildings may need retrofitting to improve energy efficiency, such as better insulation or updated HVAC systems, to address the changing climate.
- Increased risks from climate change can lead to higher insurance premiums and property devaluation, affecting the economic viability of maintaining certain buildings.
In reviewing the design wind speed map in Chapter 16 of the IBC for example, the requirements changed from the 2009 version and the 2012 code and again from the 2015 version to the 2018 code. To add to the confusion between 2015 and 2018, the terminology changed as well, from “ultimate” design wind speed to “basic” design wind speed. A handy conversion chart was also included in the codes to help “simplify” things between the two wind speeds.
In some areas, the requirement increased while other regions saw a decrease in wind design requirements. In fact, most areas of the country did see a decrease in wind speed design criteria based on the latest available data.
As an industry, we cannot expect the site requirements to remain unchanged over long periods of time, encompassing multiple code cycles. It is critically important for owners to follow potential building code changes relative to these site-specific conditions as it could impact all existing units labeled and weaken our “grandfather” provision. Remember, our code language protects only the box, not the site.
More from Modular Advantage
AI, Faster Sets, and Automation: The Future of Modular is at World of Modular
While the modular building industry has long known that it can be an effective solution to increase affordable housing, the word is slowly spreading to more mainstream audiences. Three presentations at this year’s World of Modular in Las Vegas hope to provide insight and direction for those seeking a real solution to the crisis.
An Insider’s Guide to the 2025 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) event back to Las Vegas, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education. Over the course of the conference’s four days, there will be numerous opportunities for attendees to connect, learn, and leverage event resources to get the most out of the conference.
Affordable Housing Now: The Industry’s Best Bring New Solutions to World of Modular
While the modular building industry has long known that it can be an effective solution to increase affordable housing, the word is slowly spreading to more mainstream audiences. Three presentations at this year’s World of Modular in Las Vegas hope to provide insight and direction for those seeking a real solution to the crisis.
Opportunities for Innovation in Modular Offsite Construction
Modular Offsite Construction has already shattered the myth that it only produces uninspired, box-like designs. Architectural innovations in module geometry, configurations, materials, and products make it possible to create visually stunning buildings without sacrificing functionality or efficiency.
Safe Modular Construction with Aerofilm Air Caster Transport
In collaboration with Aerofilm Systems, Heijmans developed innovative skids using air caster technology for moving modules easily and safely. These pallets are equipped with an auto-flow system, making operation extremely simple.
Miles, Modules, and Memes: Building a Modular Network One Flight at a Time
At the end of the day, social media is just another tool for building connections, and like any other tool, needs to be used skillfully to work properly. Use social media thoughtfully, and it will open doors to real opportunities and relationships you didn’t even see coming.
Falcon Structures: Thinking Inside the Box
Some of Falcon’s latest projects include creating container solutions for New York’s Central Park and an East Coast professional baseball team. More and more, Falcon is shipping out container bathrooms and locker rooms to improve traditionally difficult work environments, like those in oil and gas or construction.
UrbanBloc—From Passion to Industry Leader
UrbanBloc specializes in three main categories or markets – what they call “Phase 0” projects, amenities, and urban infill. Clients are often attracted to shipping containers because from a real estate perspective they are considered an asset. Having the flexibility to move and transport these assets allows owners to respond to different circumstances in a fluid manner that they can’t get with standard construction.
The Hospitality Game-Changer
“Hospitality is about more than just providing a service – it’s about delivering an experience,” says Anthony Halsch, CEO of ROXBOX. “And that’s where containers thrive. They allow us to create spaces that are unique, efficient, and sustainable.”
Container Conversions Counts on Simplicity to Provide Critical Solutions
Container Conversions has fabricated and developed thousands of containers for varied projects, including rental refrigeration options, offices, kitchens, temporary workplace housing, and mobile health clinics.










