By the Numbers
Assessing MBI Member Training, Professional Development & Workforce Needs

Heather Packard is the Workforce & Professional Development Director for the Modular Building Institute
As part of MBI’s continuing efforts to expand the footprint of the commercial modular construction industry, we launched an intelligence gathering process in mid-September 2023 to collect information on member companies’ challenges and needs with respect to training, professional development, and workforce. The purpose of this process was to identify critical needs to support development of a near- and long-term strategy to address these needs.
Intelligence Gathering Process
The intelligence gathering process included two phases: a qualitative phase consisting of one-on-one conversations with representative member companies and a quantitative phase consisting of a survey instrument distributed to all MBI contacts.
To ensure a representative set of data for the first, qualitative, phase, conversations were held across member company types including manufacturers (5 direct and 3 wholesale), dealers/fleet owners (3), owners/developers (2), contractors/builders (3), design professionals (3), suppliers of services (1), and suppliers of materials (2).
This phase probed challenges member companies are experiencing at an industry-wide, company-specific, and partner-specific level as well as ideas on how MBI could support attracting new entrants to our industry along with training and professional development opportunities for staff.
Visualized results from one question of MBI's Workforce and Professional Development survey from September 2023.
Qualitative Outcomes
Challenges at an industry-wide level uncovered during the qualitative phase included labor – limited supply of skilled tradespeople as well as experienced architects, engineers, and project managers – along with a lack of stakeholder awareness of modular capabilities, including clients, architects, and financial institutions.
Company-specific challenges also included labor – difficulties in attracting tradespeople, backfilling at mid and senior levels, and small talent pools for design, drafting, estimating, and purchasing – along with market supply and demand and finding new areas of growth.
Partner-specific challenges uncovered insufficient production capacity at the manufacturer level and a need for increased awareness and education amongst stakeholders including developers, lenders, building inspectors, general contractors, and clients.
Training and professional development ideas discussed included opportunities to leverage Introduction to Commercial Modular Construction for employee on-boarding and developing training for commercial modular set and install staff, sales staff, project management staff, and market-facing individuals. The one-on-one conversations also uncovered a need for building code-based training and refreshers for MBI member companies, government officials, and financial institutions.
Ideas for attracting new entrants centered on increasing youth awareness of the commercial modular construction industry’s opportunities and advantages over traditional construction. These discussions included potential outreach and engagement opportunities directed towards high-school level groups promoting trades and with vocational technology centers in an effort towards increasing the future talent pipeline for labor and trades. Outreach and engagement with universities offering a construction-related degree was another hallmark of these conversations, with a goal towards increasing university program curriculum focus on modular in the hope that this could lead to better-trained and more well-rounded future designers, architects, engineers, and project managers.
Quantitative Phase
We used a survey instrument for the second, quantitative, phase, which was distributed to all MBI contacts. To date, we have received responses from 68 unique organizations across all MBI membership categories and affiliations, a roughly 12% response rate. The survey instrument addressed the following topics:
- Estimated workforce needs over the next 1-3 years
- Most difficult roles to fill within the past 1-2 years
- Longest time it has taken to fill vacant roles
- Most useful recruiting methods
- Educational topics of interest
- Learning format preferences
Quantitative Outcomes: Estimated Workforce Needs
Current responses to estimated workforce needs across administrative and office professional staff demonstrate a near-term (next 1-3 years) need for the following roles:
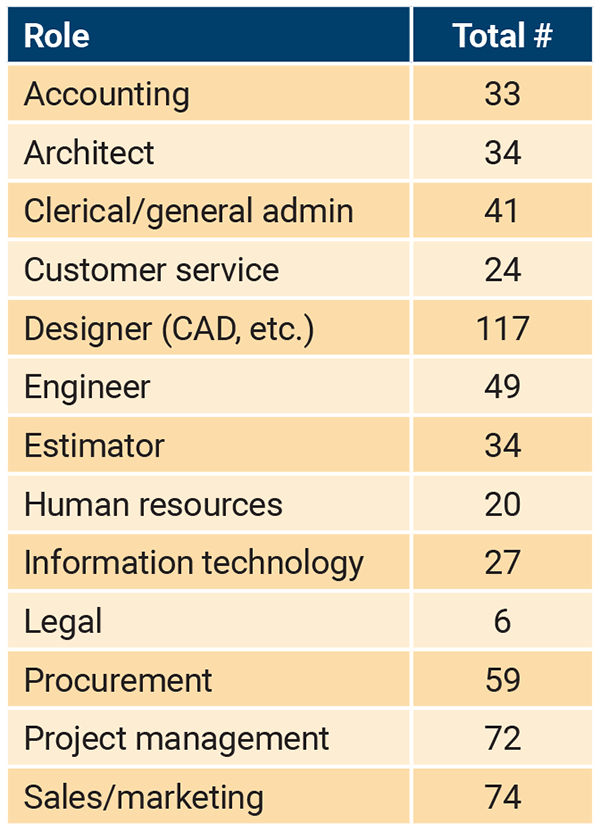
Current responses to estimated workforce needs across labor, trades, and delivery staff demonstrate a near-term (next 1-3 years) need for the following roles:
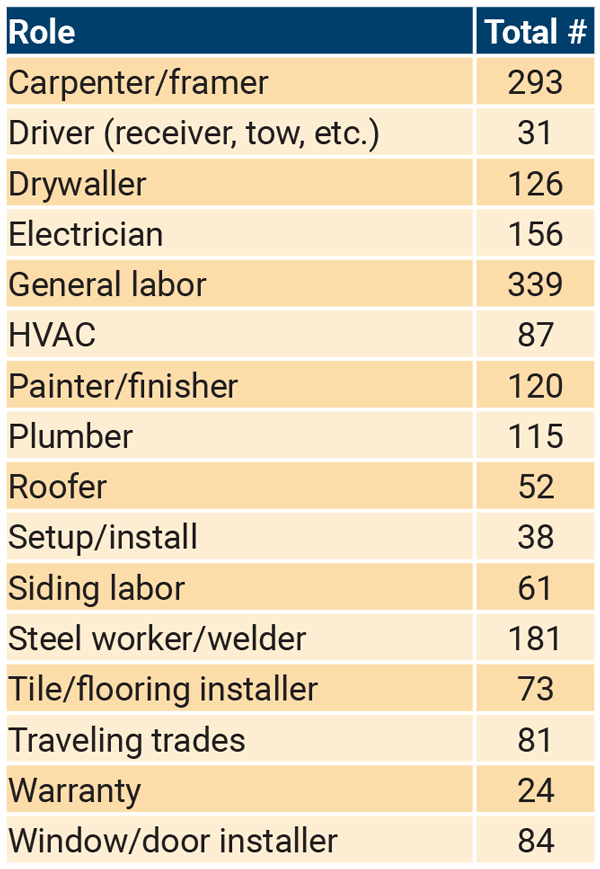
Current responses to estimated workforce needs across safety, compliance, and quality assurance/control staff demonstrate a near-term (next 1-3 years) need for the following roles:

Quantitative Outcomes: Most Difficult Roles to Fill, Longest Time to Fill Vacant Roles, and Most Useful Recruiting Methods
The most difficult roles to fill within the last 1-2 years echoed the small talent pools uncovered in the first, qualitative, phase, and included tradespeople of all types, general and skilled labor, carpenters/framers, drywall finishers, experienced production and plant workers, architects, designers, engineers, and project managers – with experience in modular – as well as drafters, BIM experts/managers, sales professionals, customer service, and estimators.
Responses to the longest time to fill vacant roles further demonstrate the talent shortage our industry is experiencing. Roles for CAD operators and designers, electricians, plumbers, welders, and quality control staff were reported to take greater than 1 year to 2 years to fill.
Members reported word of mouth and referrals from current employees as the most useful recruiting method, followed closely by social media efforts and job boards (typically Indeed for labor and trades). The full list of recruiting methods, their current rankings, and responses to “other, please specify” is below.
Quantitative Outcomes: Topics of Interest and Learning Format Preferences
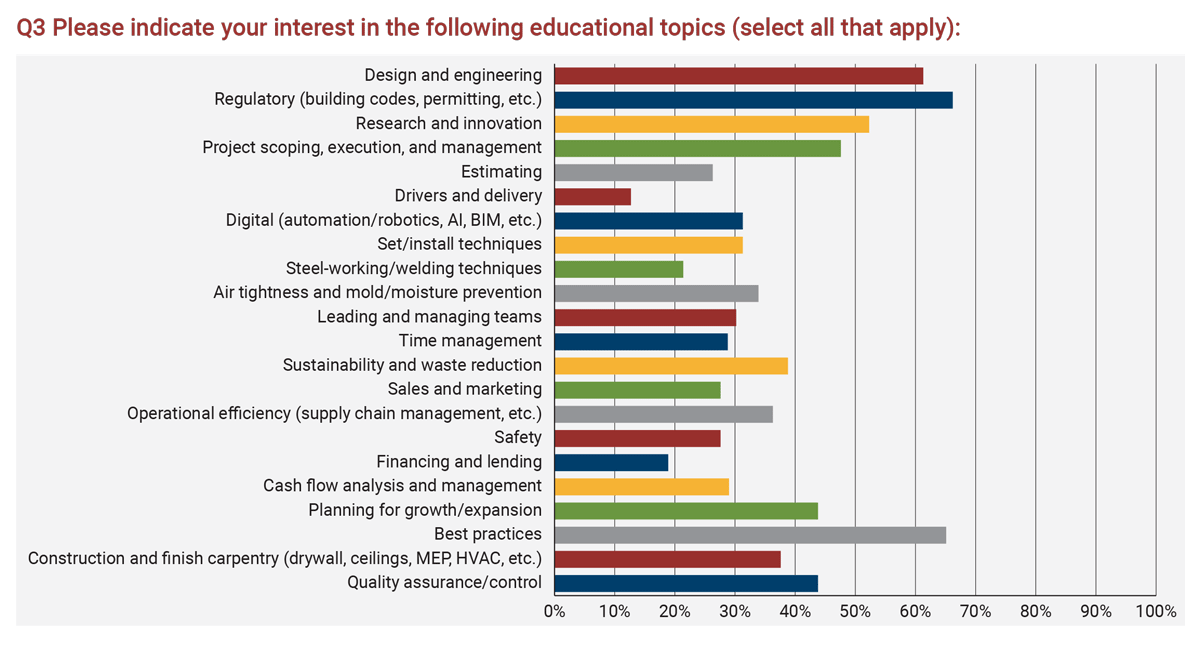
In terms of learning topics of interest, members reported an interest in regulatory topics including building codes and permitting, best practices in the industry, design and engineering, research and innovation, project scoping, execution and management, planning for growth and expansion, and quality assurance and control. The full list of learning topics of interest and their current rankings is below.
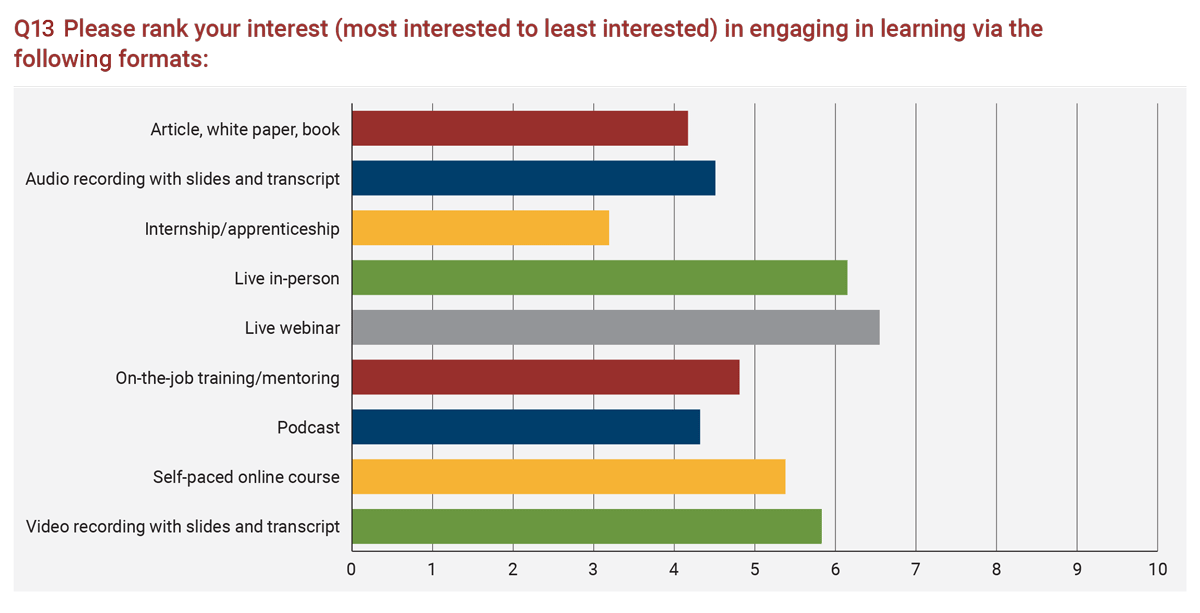
Lastly, members expressed a preference for live webinars, live in-person events, video recordings with slides and transcripts, and self-paced online courses. The full list of learning formats and their current rankings is below.
Make Your Voice Heard
The survey instrument will remain open so that we can continue to collect member needs and preferences and take these into account for further strategy development and execution. Please visit MBI's online survey and make your voice heard!
If you have any questions about the process or have other feedback or suggestions for MBI to consider, please contact Heather Packard, Professional & Workforce Development Director, at heather@modular.org.
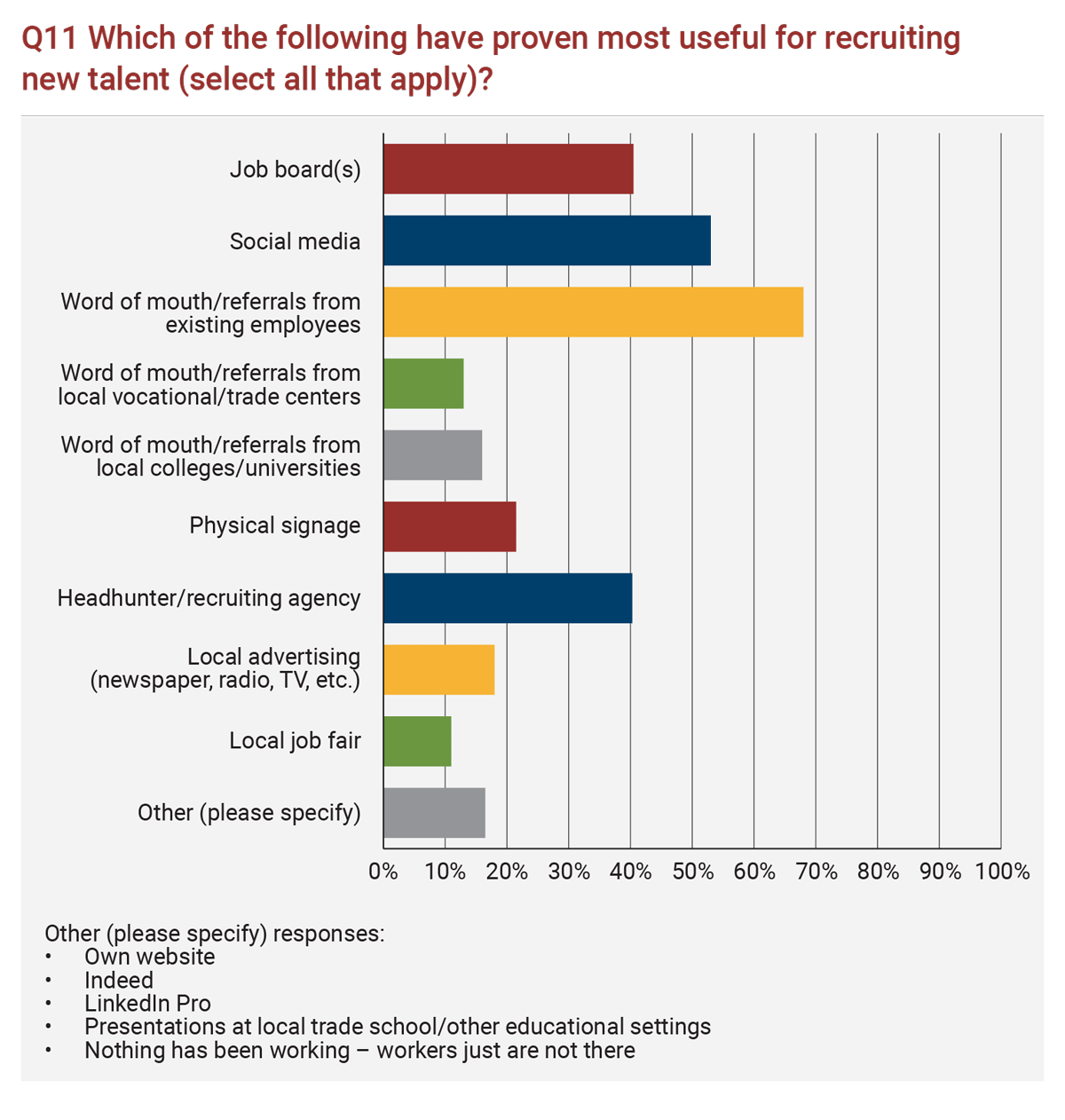
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.