The Envelope Insulation Design Regarding Material Alteration Compatibility in Blast-Resistant Modular Buildings

Ran Yu is an arcitect with GLMV Architecture
Blast-resistant modular buildings (BRM buildings) are designed with strong steel exterior wall structure and thick steel skins to withstand blast events and to protect people and equipment from explosions. They are commonly used in oil refineries, chemical processing plants, laboratories, and similar operations.
However, the intrinsic high thermal conductivity of the steel skin and structure in exterior walls acts as the cold bridge reducing the efficiency of building envelope insulation. This results in the need for more insulation material and thicker insulation layers for BRM buildings to comply with building energy code. As energy code and energy-saving standards are adopted by more and more jurisdictions, the requirements for energy code compliant building envelope insulation design have increased.
Meanwhile, the module dimension of modular buildings adopts the inherent limitation of transportation. The prevailing transport limit is 12 feet wide and 40 feet long. A modular unit exceeding this limitation will result in a significant increase in shipping costs.
The third challenge of BRM insulation design is the suddenly derailed global supply chain with price and availability uncertainty. Following the pandemic, the existing global supply chain developed over the past decades was challenged and forced to reshuffle within a few years. The construction industry is experiencing insulation material shortages and incredible price increases. This leads to three possible results: spending extra time and money to redesign and revise drawings with alternative insulation materials; increased construction budgets; postponement or cancellation of projects.
Thus, BRM envelope insulation configuration has impacts on construction schedule time, potential redesign workload, and market competitiveness, which are all critical to the success of a BRM project. One must ask then, how to design an envelope insulation fitting in BRM exterior wall, being compatible with material alteration without wall thickness increasing?
The Envelope Insulation Design Regarding Material Alteration Compatibility
Design for material alteration compatibility aims to reduce redesign, project postponement and cancellation by thinking ahead. At the outset of a project design, consider various insulation material options and thicknesses available
and their impact to energy code compliance. This allows better coordination with blast-resistant structural design requirements. Different than using determined insulation material, design for material alternation compatibility requires the study of various insulation material properties, unit price, and their compatibility with current factory equipment and worker’s skill. The design process is below:
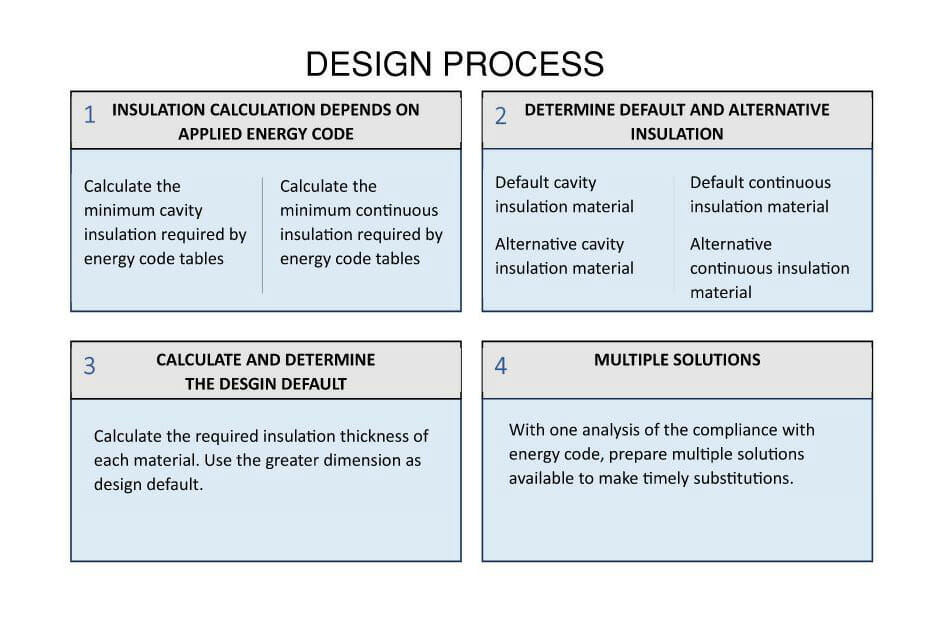
- Insulation calculation depends on applied energy code.
(1) Calculate the minimum inorganic cavity insulation between steel framing required by energy code tables.
(2) Calculate the minimum continuous insulation required by energy code tables. - Determine default and alternative insulation materials.
In BRM buildings, to achieve energy code compliance, cavity insulation is needed in between steel framing, and continuous insulation is needed to be attached to the inner side of steel structure. All these are done without changing BRM’s inherent structural characteristics. At least two materials each for the cavity and the continuous insulation shall be selected.As an example of material selection, one may use close-cell spray foam or mineral wool as cavity insulation, while using polyisocyanurate rigid board or extruded polystyrene board as continuous insulation.
- Calculate the required insulation thickness of each alternative material. Use the greater dimension as design default.
- Now with only one analysis of the compliance with energy code, we have multiple solutions available to make timely substitutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, design BRM building envelop insulation with compatible to alterative materials supports the success of BRM projects by reducing postponement and cancellations due to redesign work and time, controlling project budget and time.
These advantages will benefit all stockholders including building owners, contractors, manufacturers, and designers.
More from Modular Advantage
Homes as Essential Infrastructure
The housing crisis is nothing new. Across the world, federal, state, and municipal governments of all sizes are struggling with how to provide more affordable housing—quickly—to those who need it. In Canada, Paul Halucha, Deputy Minister of Housing, Infrastructure, and Communities Canada (HICC), argues that the federal role in housing has shifted from funding at arm’s length to actively shaping outcomes.
Building the Future, Offsite
In the face of a national housing crisis, England stands at a critical inflection point where innovation, scale, and public-private partnerships must converge to meet an urgent need: more homes, and fast. Homes England is helping reshape the housing market by actively supporting MMC through a strategic blend of land development, financing, and grants.
How POJI and MOKO Are Industrializing Modular Construction Through Automated Engineering Systems
Working with Scandinavian Industrialized Building System (SIBS), POJI and MOKO helped realize a modular city concept located in Järfälla municipality of Stockholm, Sweden, with 350 apartments, communal areas, restaurants, small shops, and a preschool in a pleasant mix with experiential architecture and greenery.
Inside Boutique Modern’s Mission to Make First Homes Affordable and Efficient in The U.K.
The U.K.-based firm has been in business for 12 years, manufacturing houses for both private clients and local government, with a large chunk of its business coming from “affordable” and social housing. Working in a 32,000 square-foot factory in Newhaven, Sussex, Boutique Modern is changing decades-old thinking about constructing houses, all through the use of modular.
BoulderMOD: Producing Affordable Modular Homes While Training the Workforce of the Future
Colorado has been hit with a double whammy—a decline in the number of skilled construction workers and an increased need for affordable housing. BoulderMOD, a partnership among the city of Boulder, Flatirons Habitat for Humanity, and Boulder Valley School District, is tackling both problems and helping others do the same.
Guerdon: Seeking the ‘Holy Grail’ of Modular Construction
Guerdon, a modular manufacturer in Boise, Idaho, recently won what Laurence (Lad) Dawson, CEO and Managing Partner, describes as the ‘holy grail’ for a modular manufacturer. The RFP calls for a pipeline of six projects, totaling approximately 570
units.
State of Modular in 2025: Facing Reality
The critical and urgent reality is that the modular industry needs to open the doors to collaboration across all sectors. The sooner we stare down these challenges, the sooner we can welcome a new reality where modular is the dominant way to deliver housing for better performance, quality and all at a lower cost.
Modular Multifamily Housing as a Scalable Solution to the Housing Crisis
GreenStaxx provides a real-world, scalable solution through its standardized library of modular-ready multifamily designs and its innovative triple-decker model. Together, these offerings address the industry’s two greatest needs: efficiency and adaptability. By focusing on quality, repeatability, and collaboration, GreenStaxx is helping move modular construction from niche to mainstream and offering a practical path toward solving the housing shortage.
Sealed for Success: The Role of Waterproofing in Modular Construction
Water is one of the biggest threats to any building, causing structural damage, mold growth, and costly repairs if not properly managed. Waterproofing is the first line of defense, ensuring durability and long-term performance. As construction methods evolve, so do waterproofing solutions – moving beyond traditional coatings to advanced, factory-ready systems.
From Volume to Velocity: Scaling Multi-Family Projects Without Losing Control
When projects grow too fast without the right systems, factories run into problems. They miss deadlines, crews burn out, and quality drops. Instead of steady progress, chaos takes over. Things slow down, even with more units going through. That’s because building more isn’t enough—you also need to build smarter. That means shifting focus from volume to velocity.