Hacking Construction and Making it Greener at BOXY


Mateo and Tiago Atwi are the CEO and COO, respectively, of Louisiana-based BOXY LLC.
Born and raised in Louisiana, young brothers, Mateo and Tiago Atwi, are eager to — as they put it — “hack the construction industry”. Not in the layperson’s sense of criminal hackers who exploit cyber-security weaknesses, but in the sense commonly used in the tech world: Overcoming obstacles in creative, non-standard ways in order to achieve surprising results.
They’re putting the hacker mentality into practice to come up with solutions to problems the construction industry may not have even realized were problems. “There are different ways to hack the sales cycle, designing, estimating, procurement, materials, labor — all the steps of a project,” Mateo says. “Instead of doing things the same way, let’s be creative and find new, sustainable ways to achieve better results both during construction and afterwards.”
The brothers founded BOXY just last year and the company is currently finishing a rural health clinic in Louisiana, built with cold-formed steel modules. It’s a five-room, 1500 square feet expansion of an existing clinic. “The design is a little different from what’s typical. In volumetric construction, you usually have a lot of redundant back-to-back walls,” says Mateo. “Instead, we put a panelized hallway between our pre-finished modules so that all the module walls are separated and useful. We’re building the roof on-site.”
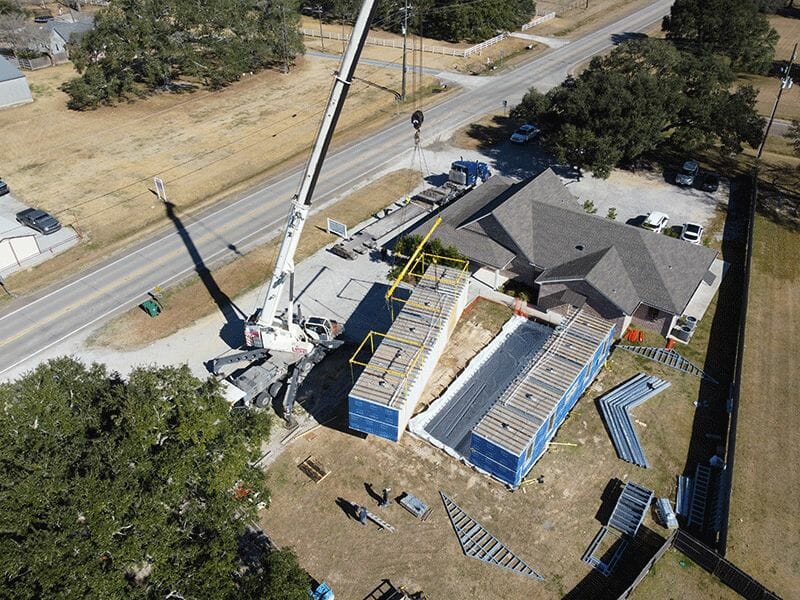

BOXY’s two-module rural health medical clinic project being set in Church Point, Louisiana. Since rural health clinics go to remote places, it makes sense to build them in metro areas and ship them.
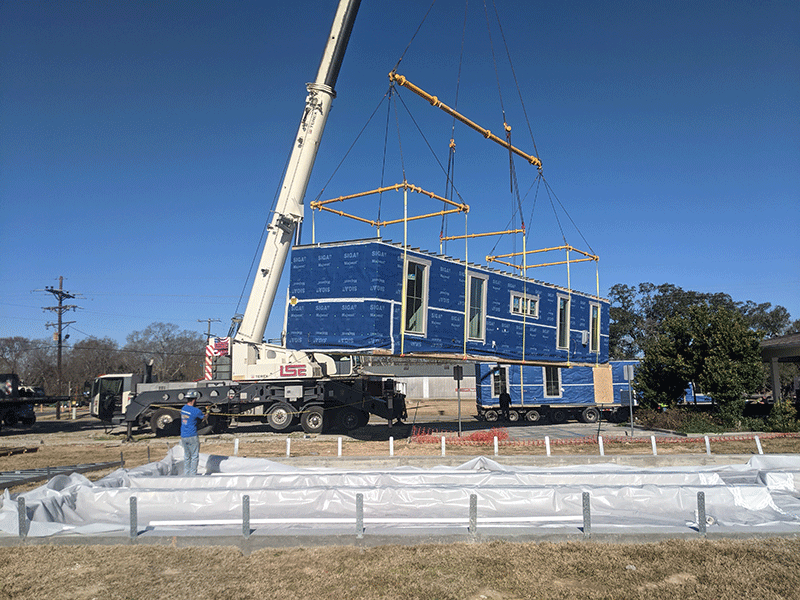
Elaborate rigging is required to minimize the bending in the modular cold formed steel units. This 52’ unit has five straps from a modular lift system manufactured by Modulift.
For this project, they had difficulty finding a general contractor who was knowledgeable about installing modules and who was interested in performing the relatively small project. So they acted as general contractors themselves, which also satisfied their desire to control the whole process from beginning to end.
First Tastes of Prefabricated Construction
Before founding BOXY, both brothers gained experience at BMarko Structures, a modular manufacturing company in Georgia. They also had experience with other kinds of prefabrication and manufacturing.
Mateo went to Georgia Tech to study mechanical engineering, graduating in 2019. He had two internships at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Texas and also interned at a jewelry manufacturer in Louisiana. During this time, he was exposed to lots of R&D and manufacturing. After graduating, Mateo worked in various positions at BMarko, including Vice President of Operations.
Graduating in 2018, Tiago also studied mechanical engineering, along with math, at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette. His primary interest is sustainability, and he’s worked with renewable energy companies in Spain and in Texas. His first taste of prefabrication was as the Field Engineer for a wind farm project about two hours from Austin. “It was so fast and efficient. We stacked all the components for 110 wind turbines and assembled them on-site. It took four months to build a wind farm to generate enough power for 400,000 households,” Tiago says.
He then saw the work Mateo was doing with upcycled shipping containers at BMarko. “It was the same kind of idea. Taking factory-manufactured components and assembling them on-site. If you can figure out the logistics and the crane system, it’s such an efficient way to build.”
Tiago joined Mateo at BMarko for a few months before the pair decided to move back home to Louisiana to found their own modular company.
Sustainability
Tiago notes that there are numerous factors influencing the carbon impact of construction, such as “the materials used, waste generated, subcontractors driving to the site” and so on. Over a building’s lifecycle, “the insulation and how air-tight it is makes a difference to how much energy the building uses. And the materials you use makes a difference to how long the building lasts. Offsite construction is effective for really optimizing the specifics to reduce buildings’ carbon impact,” Tiago says.
An important consideration is how durable a building is, and that can depend on where it’s located. “During construction, you may not see a big difference in carbon impact between building with wood and building with steel,” Mateo says. “But here in Louisiana, the base flood elevations are very high, so there are issues with termites and rot in wooden buildings. So, in this environment, steel buildings are more durable. Wooden buildings are more wasteful because they have to be demolished and re-built sooner.”
Part of BOXY’s agenda is to design to meet passive house standards, with better building envelopes and insulation, thus reducing energy usage over a building’s lifecycle.
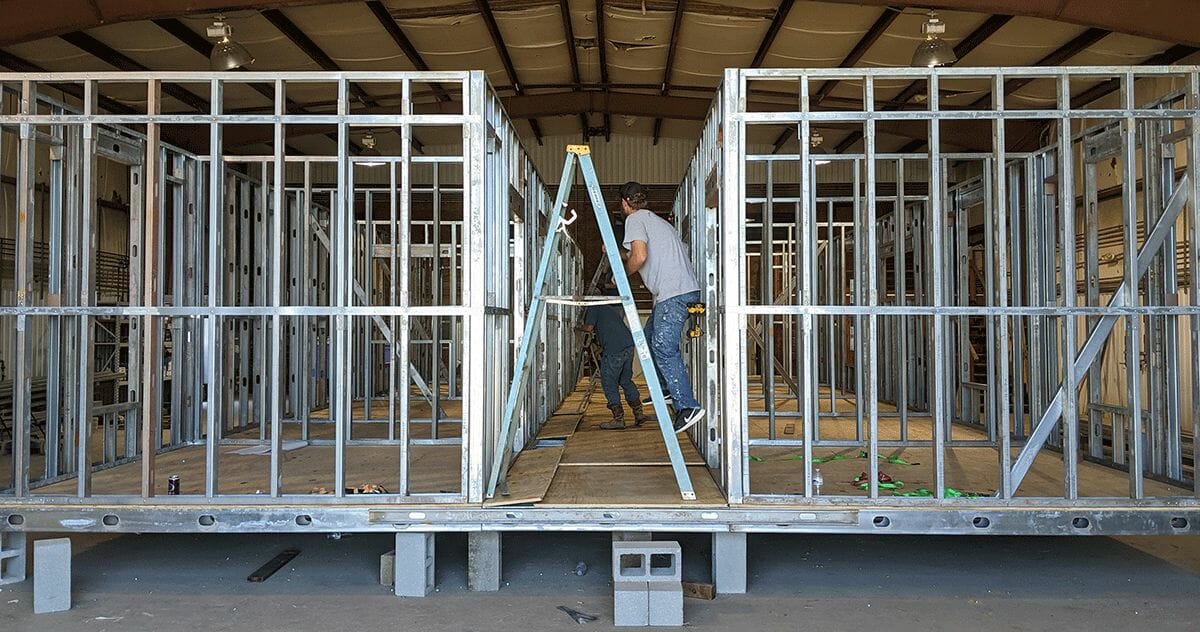

Construction as Manufacturing
At the broadest level, the Atwis’ goal for BOXY is “to have a big, positive impact for the people who work in the construction industry, now and in the future,” Mateo says. “And also for the people who live and work in the buildings.” To achieve these big goals, Mateo says their strategy is to “design buildings with repeatable systems, and bring manufacturable elements to construction.” They’re doing this in a number of ways:
- Using manufacturing processes like CNC roll-forming that are design-driven (in contrast with labor-driven on-site processes).
- Creating an engineering library of repeatable designs that have been tested through execution.
- Designing repeatable framing kits with a Revit plugin, AGACAD.
- Creating software and setting up a website, usframefactory.com, for stud and track sales where customers can get instant pricing and lead times on custom framing materials.
Hacking the Sales Cycle is Greener
One example of hacking the construction industry is re-thinking how buildings are sold. “The sales cycle doesn’t have to mean a lot of time spent on the phone or emailing. We’re hacking the sales cycle by selling materials, such as metal track and studs, and frame kits online,” Mateo says.
Not only does this online ordering system save customers’ time, it also reduces waste. Because BOXY doesn’t charge any additional fees for ordering custom lengths, customers can order the exact amount they need. “This means subcontractors can remove the normal 10-15% waste factor they typically include,” Mateo explains. “There’s a significant amount of embodied carbon in wasted materials, so reducing waste helps reduce the carbon impact of the building. At the end of the day, it also saves the subcontractor and their client money.”
World of Modular Presentation
In their World of Modular presentation, Mateo and Tiago Atwi will delve into more detail about how the construction industry can learn from the software industry and apply some of its practices
About the Author: Zena Ryder is a freelance writer, specializing in writing about construction and for construction companies. You can find her at Zena, Freelance Writer or on LinkedIn.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.