Inside the Modular Building Process
In this article, each step of the modular construction process will be explored and reasons for these advantages will be detailed.
The Advantages of Modular Construction
Modular construction (also referred to as off-site and/or volumetric construction) is growing in popularity because it offers several advantages over traditional construction. Chiefly, these advantages include:
- Shorter construction times (leading to a quicker ROI for owners), and
- Cost certainty (obtained through fewer mid-project changes and weather delays, and, to a lesser degree, fewer on-site injuries)
These advantages are obtained through a carefully planned design and construction process. Unlike many traditional construction projects, modular construction leverages a precise timetable and a predictable, industrialized assembly process to realize its value.
Step 1: Design approval by the regulating authorities and end users
In the modular building process, the project begins at the design phase. Architects and engineers, using building information modeling (BIM) systems and other software, create exterior and interior plans. Once plans are approved by the owner, they are submitted to the locality or third-party service for approval and building permit applications are submitted. The manufacturing of components begins once the design is finalized.
Note: Modular buildings must follow the local building codes and zoning regulations. The modular building contractor should already know the regulations that apply to the project based on the address of the physical building site and the agencies that have jurisdiction over that area.
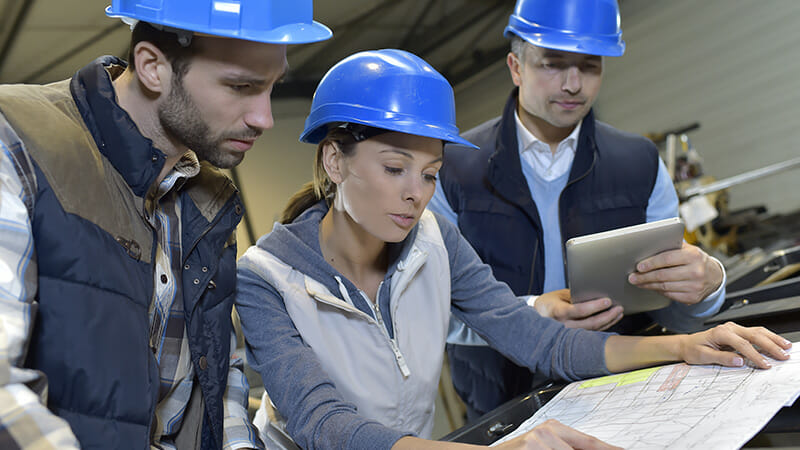

Modular buildings must have approved and finalized designs before construction begins.
Step 2: Construction of modular components in a controlled atmosphere
The module components are built in a controlled offsite factory environment while site excavation and grading is going on at the same time. The amount of work (60% - 90%) performed in the factory can vary based on owner requirements. For example, it can include assembling basic structural components (like exterior and interior walls, flooring, and windows), installing mechanical, plumbing, and electrical components, and completing interior finishes such as drywall and cabinets. Because so much can be accomplished off-site, the labor force in the factory can consist of any or all of the following:
- Carpenters
- Drywall finishers
- Plumbers
- Electricians
- HVAC workers
- Painters
- Floor finishers, and more
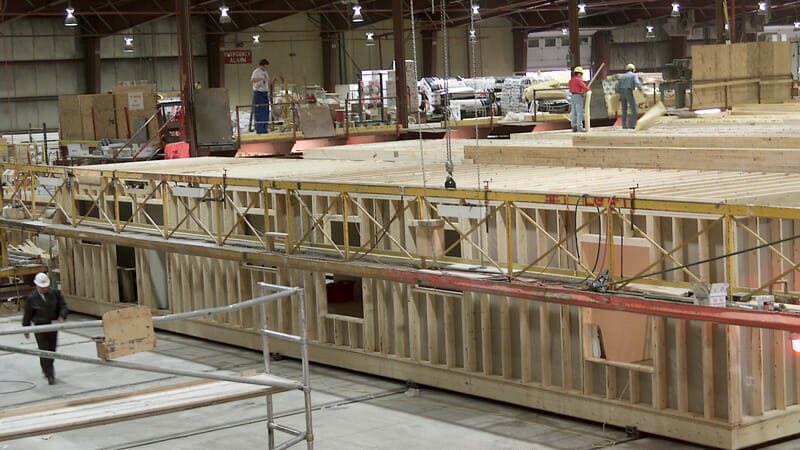

A controlled factory environment allows modules to be built quickly, precisely, and more safely.
Inspections by a third party or other building code official takes place at various stages in the factory. Upon completion of the modules, they are prepared for transportation.
Step 3: Transportation of modules to a desired location
Modular buildings are shipped on chassis integrated into the structure or carriers towed by trucks. Due to the need to transport the modules to the final site, each module must be built to independently withstand travel and installation requirements (e.g., high winds, manipulation by cranes). Of note, the resiliency of the individual modules contributes to the greater structural strength of the final building, another advantage of modular construction.
Transportation of the modules depends upon some important factors such as the cost and method of transport, travel distance, and weight. It usually isn’t feasible to ship modules far due to road size and load restrictions. Generally, the maximum desirable distance for transportation of modules is 250 to 400 miles. The costs and transportation difficulties greatly increase for building sites farther than 400 miles.
The maximum width, height, and length of individual modules that can be transported is dependent on several criteria including local Department of Transportation restrictions; bridges, overpasses, utility lines that cross over roadways; and the actual route itself from the factory to the final destination. For ease of transportation, modules commonly have measurements of 15-feet wide, 12-feet high and 60-feet long, although these measurements can differ greatly in any direction based on a number of factors.
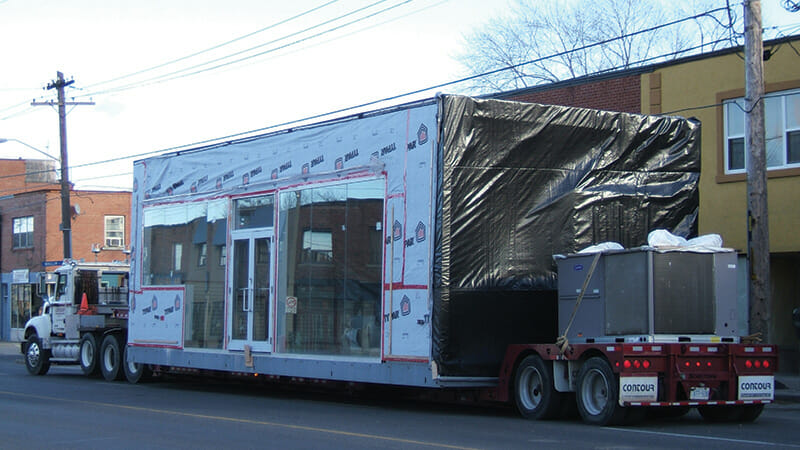

Transporting the finished modules to the jobsite can involve a single truck or many, depending on the size of the project.
Step 4: Erection of modules to form a finished building
Once at the jobsite, the modules are stacked by crane or rolled onto the foundation, bolted together and sealed for weather-proofing. The modules are then connected together, utilities are hooked-up, exterior siding and roofing components are completed, and site work is finished. The final construction stage includes completing exterior systems such as cladding, final caulking and sealing, adding stairs and elevators, and competing any interior elements such as painting, trim, cabinets, countertops, and installation of appliances that didn’t occur in the factory.
Modular construction offers an accelerated schedule for designers and builders and an accelerated ROI for owners. This is primarily accomplished by working on multiple fronts simultaneously. While modules are built and furnished in a controlled offsite location, site work can occur at the same time, eliminating the need for less efficient, strictly linear process.
This process—called parallel construction—is a key benefit of the modular construction process as it allows for reduced construction times of about 30% - 50% that of conventional construction.
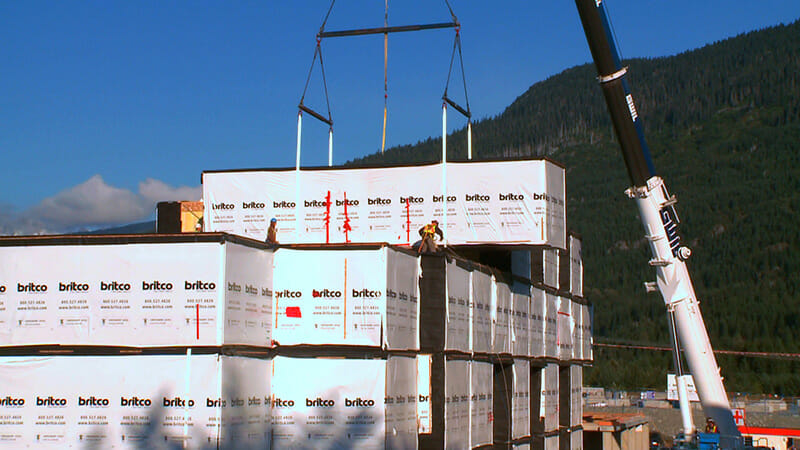

Installing the modules happens quickly. In some cases, large multi-story buildings can be stacked in less than two weeks.
The process of modular construction is strict. Plans must be finalized early and stakeholders must have a complete understanding of the entire building process, but the advantages of modular construction are indisputable. To find a modular builder near you, click here.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.