Lightweight & Beautiful 3D Printing

John McCabe is the Advanced Concepts Designer at Branch Technology, recently transitioning into that role from the Director of Marketing position at the company. McCabe has a Bachelor’s Degree in Architecture and a Masters in Industrial Design. He taught design at various institutions before moving to Branch in 2019.
Offsite Advantages
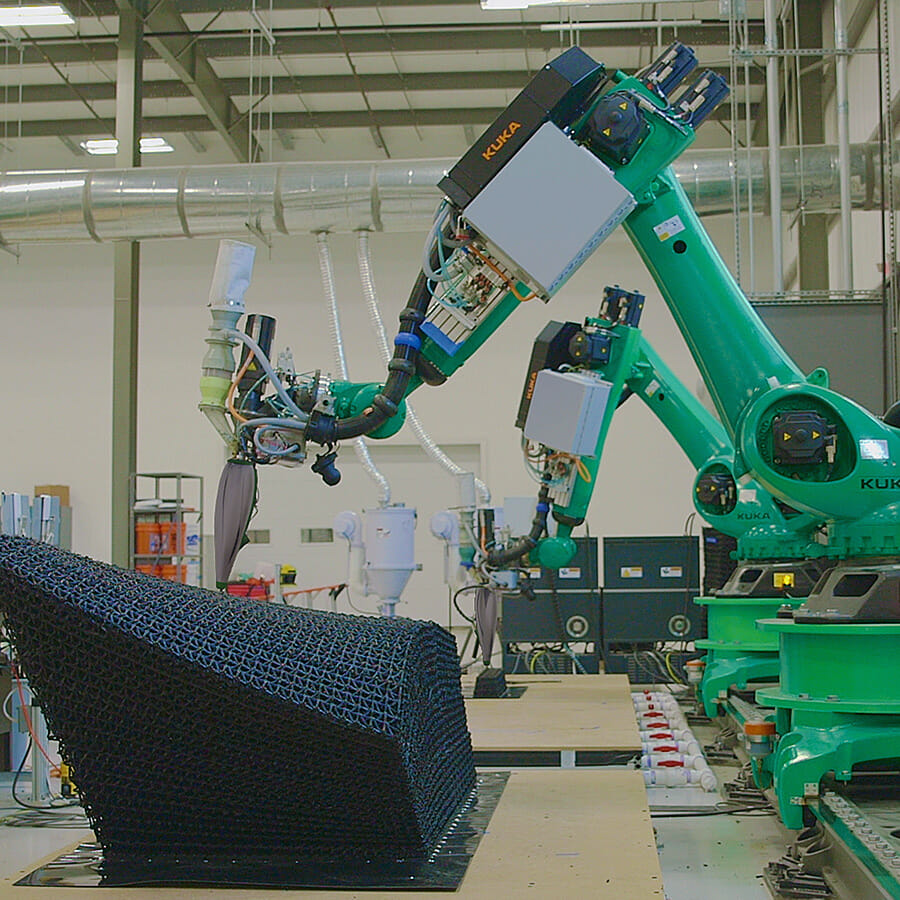
When you think of 3D printing buildings, you probably picture giant outdoor robot gantries “pooping out concrete” as John McCabe of Branch Technology puts it. Layer upon layer, gradually building up the walls “as has been done for millennia” — only now with robotics.
Branch Technology does 3D printing very differently, starting with printing offsite. “Printing onsite adds chaos, where there’s already a lot of safety issues,” says McCabe. Branch’s facility is far from chaotic — it’s a precise robotic ballet, with multiple projects being coordinated at the same time.
“In our facility, we have 12 foot robots printing a range of different types and scales of projects. One might be working on part of a parking deck, and another might be working on a bank, while another is printing something for the Department of Defense.”

Special Structures
The structures that Branch robots print are also very different from layers of undifferentiated concrete. They are complex lattices that can be manufactured from various substances, have many different shapes and sizes, and be filled with different materials.
“Think about it. Very few buildings are made of only one type of material,” says McCabe. “Branch processes can combine complementary materials, increasing the resulting building’s capabilities and adding value for the client.”
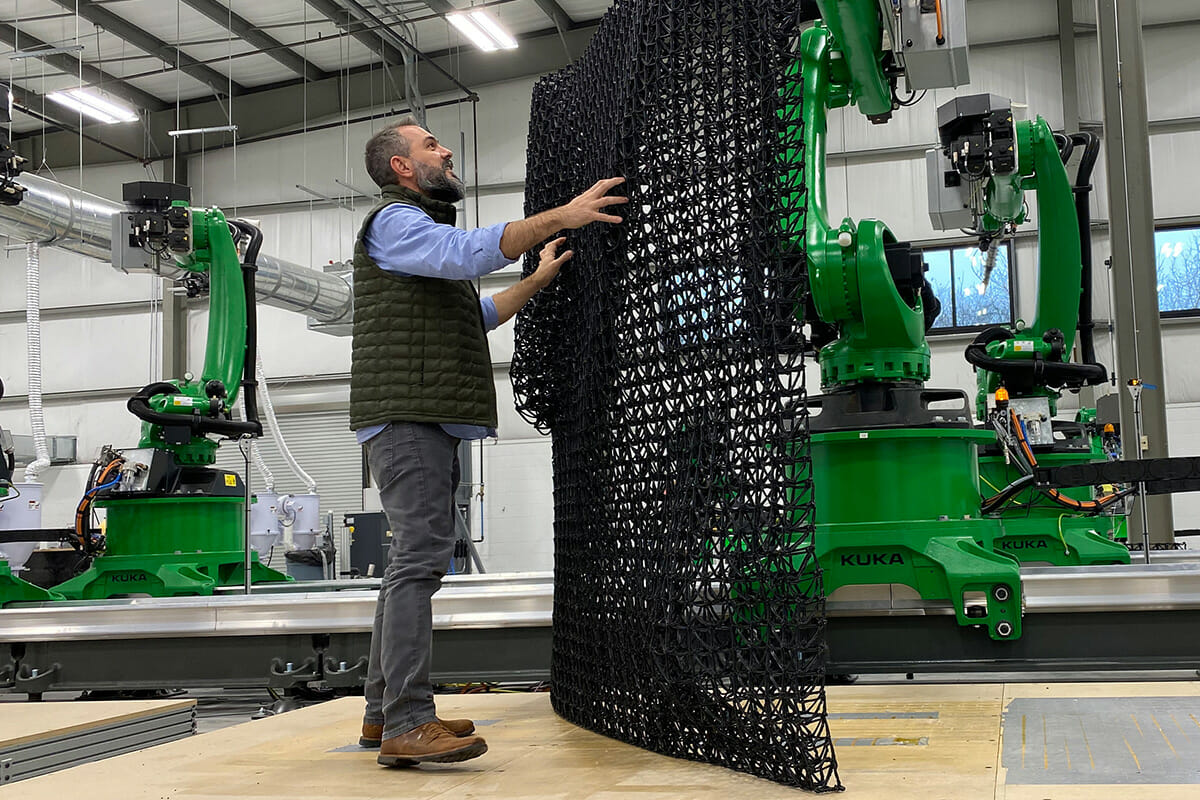

Branch’s 3D printing “uses 20 times less material than other 3D printing methods, with almost no waste” and the resulting structures are many times lighter than a similar size structure printed with concrete. Although they’re light, the structures are designed for strength too. “A matrix we print that’s the size of a concrete block — but which is 90% air — will hold 2000-3000
pounds of compressive force,” explains McCabe. “When we fill that space with a customized foam, we can get almost 10,000 pounds of compressive strength.”
The lattice structures can be filled with various materials with different properties such as sound attenuation or thermal insulation. Sensors can be embedded within the materials to create a smart building.
Branch has printed a 3,000 square foot single story house. McCabe says it’ll be a few years before they can focus on building tall, self-supporting structures because the materials currently can’t compete with the capabilities of steel. “For the same reason, it’ll also be a long time before 3D printing with concrete can build taller than one storey.”
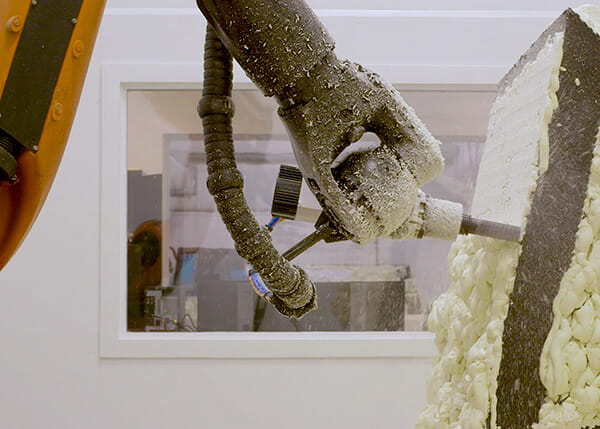
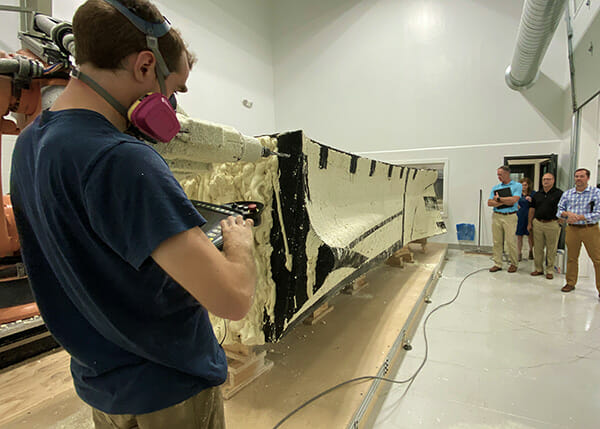



Founding and Focus
How was Branch founded? In 2013, there was a Kickstarter project for a 3D printing pen that could print in midair. Branch Founder and Chief Executive Officer, Platt Boyd, bought one and played around with it, attaching it to mini robots. He decided the idea had commercial potential in the construction industry, left the architecture firm where he’d worked for over 15 years, and moved to Chattanooga to found Branch. (Chattanooga and the surrounding area is a hotbed for innovation, especially in advanced manufacturing.)
“The company was embraced by the Chattanooga startup culture and the first employees were rockstars who came here from places like New York City and Boston. For the most part, they’re still here,” says McCabe. “We now have about 30 people working here and they’re the smartest group of people I’ve ever had the good fortune to work with.”
Because 3D printing is so versatile, Branch often received requests to make random things. But Boyd decided they needed to focus and the company went all-in on developing 3D printed façades. “They’re a great non-structural way to add a signature look to a building while still embracing the traditional construction trades.”
Labor
It’s a persistent refrain that it’s hard to hire young people to work in the construction industry, and labor shortages are a major problem. But working in the Branch facility is a far cry from a typical construction environment and Branch hasn’t had hiring problems.
“Construction companies can’t find talent,” says McCabe. “I’m privileged to work with a large, diverse group of young people who are very excited about robotics and the future of construction. They want to work in this industry.”
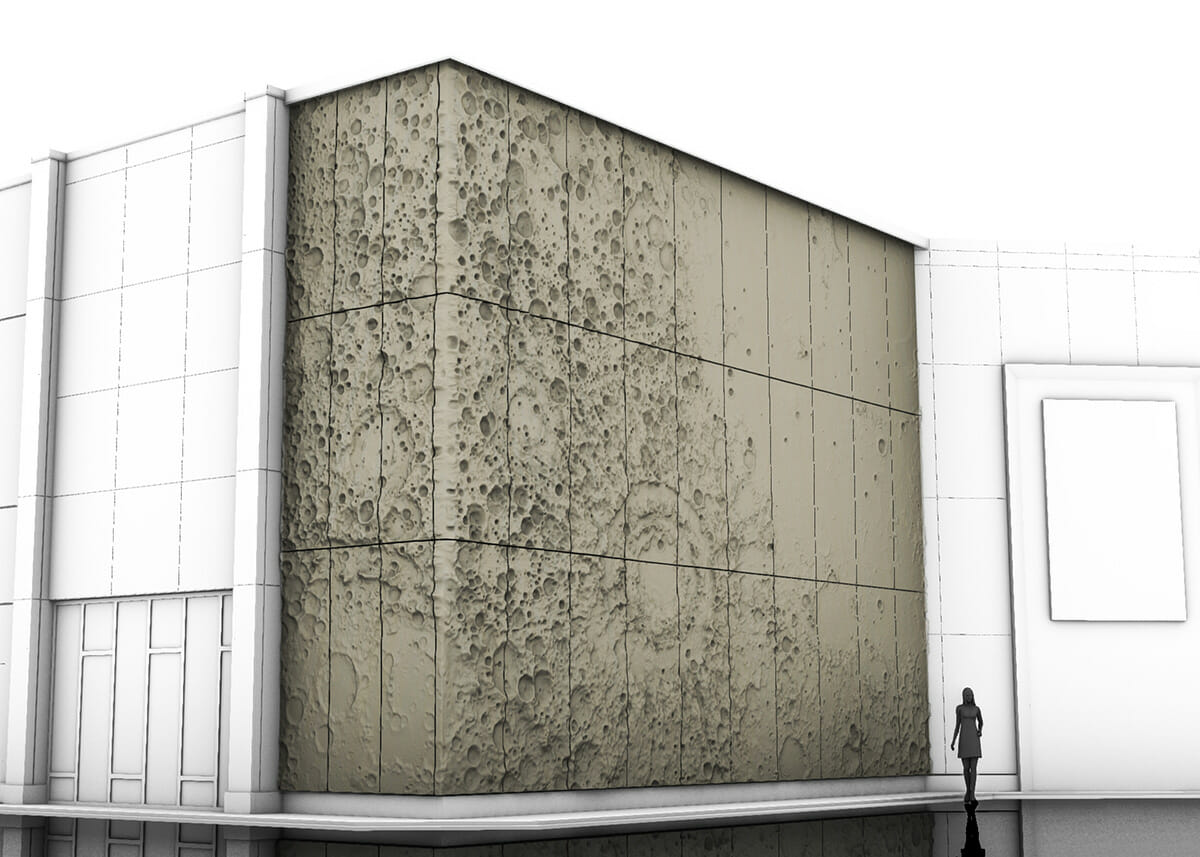

Off-World Construction
Branch has a team focused on developing solutions for the Department of Defense. “We’ve been taking speculative ideas and creating advanced manufactured products to fit their customized need,” says McCabe. “The kind of project ranges from a logistics solution for high-tech equipment, a building façade for onsite housing, or lightweight EMP-hardened expeditionary structures.”
They also work with the Air Force and the Space Force, leaning into this since 2017 when, out of a field of 77 global competitors, Branch won first place in the NASA Martian Habitat Challenge. The material they co-developed for printing the Martian habitat was the equivalent of 70% Martian soil, mixed with 30% recyclable mission waste such as bags and parachutes.
“The Space Force is expanding their knowledge and capabilities in off-world construction. We’ve been involved in developing zero-g and other-world concepts to save fuel and time, as well as to protect our service-people and equipment
from harm.”
The Future
Branch is partnering with real estate companies, developers, construction companies, and architecture firms. McCabe says that small companies trying to make their mark as well as big companies looking for efficiencies see value in Branch’s work.
“In the long term, we want a distributed factory network around the world that can print, fill, and finish structural and non-structural components for buildings of all scales,” says McCabe. “We have a roadmap to get there. We have some great partnerships in the pipeline and it’s going to blow some minds when we can finally talk about them!”
About the Author: Zena Ryder is a freelance writer, specializing in writing about construction and for construction companies. You can find her at Zena, Freelance Writer or on LinkedIn.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.